Invited
Speaker
A Novel Predictive Flip Regression Technique for Qsar of Aromatic
Substances: Egfr Inhibitory Activity of Quinazoline Analogues
Omar Deeb and Brian Clare
Palestine
Cancer in the Middle East is an important
issue in which approximately 1 in 16,385 or 0.01% are infected annually
[1]. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), identified as a kind
of protein tyrosine kinase (PTK), has been demonstrated to be related
to many human cancers leading to believe that EGFR is an attractive
target for anti-tumor drug discovery.
This study has used two relatively new techniques. (1) flip regression
[2], for handling the symmetry of the phenylaminoquinazoline system.
(2) the use of the orbital nodal angle descriptors [3-6], see Figure
1.
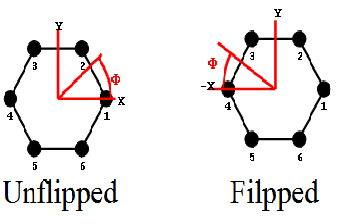
Figure 1. A benzene ring showing the calculated nodal angle
(Φ) before
and after flipping. X-axis indicates the reference point.
We found excellent regression model between the quinazoline-inhibitory
activity of 63 analogues with the selected descriptors [6] in comparison
with the results in [7]. It is envisaged that the benzene rings of
the quinazolines (Figure 2) are interacting with aromatic systems
on the receptor and that alignment occurs between the π-orbital
nodes on the pair. The proposed models provide an insight for further
designing of new anticancer drugs.
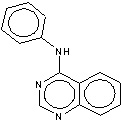
Figure 2. Quinazolines skeleton
References
[1] Freedman LS, Edwards BK, Ries LAG, Young JL (eds). Cancer Incidence
in Four Member Countries (Cyprus, Egypt, Israel, and Jordan) of the
Middle East Cancer Consortium (MECC) Compared with US SEER. National
Cancer Institute. NIH Pub. No. 06-5873. Bethesda, MD.
[2] Clare BW, Supuran CT. Bioorg Med Chem 2005; 13: 2197-2211.
[3] Clare BW. THEOCHEM 2002; 507: 157-164.
[4] Deeb O, Clare BW. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2008; 22: 885-895.
[5] Deeb O, Clare BW. Chem Biol Drug Des 2008; 71(4): 352-362.
[6] Deeb O, Clare BW. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 2008; 23(6): 763-775.
[7] Mariano P, Ivanka T, Iliza P. Int J Quant Chem 2006; 106(6):1432.
* This lecture is dedicated to Prof. Brian Clare
that Passover in August 2008.
|



