Invited Speaker
Silicon-Based Protease Inhibitors
– Advances in Chemistry and Applications
Scott McN. Sieburth
USA
The silanediol group, when incorporated into a peptide-like structure
(1), can be an effective mimic of the tetrahedral
intermediate of amide hydrolysis (6) and thereby
act as an inhibitor of proteolytic enzymes. Appropriately functionalized
silanediol structures have been found to be low nanomolar inhibitors
of aspartic and metallo- proteases.1 Inhibition of serine proteases
is a focus of our current efforts.
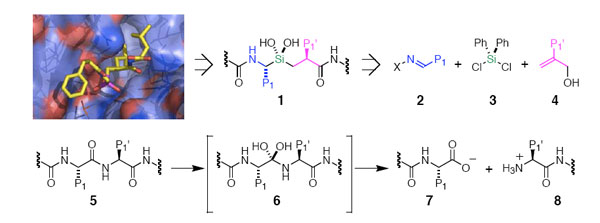
Instrumental to the exploration and use of silanediol inhibitors is
an efficient method for their assembly. The first synthetic methods
were linear and labor intensive. We are developing short asymmetric
sequences using readily available components (2 – 4),
employing both asymmetric catalysis and chiral auxiliary-based methods,
to fully control the stereochemistry in both the -amino silane component
(blue) and -silyl acid portion (magenta).
The state-of-the-art in silanediol protease inhibitor synthesis and
applications will be described.
1.S. McN. Sieburth & C.-A. Chen, "Silanediol Protease Inhibitors:
From Conception to Validation" Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006,
311-22.
|



